Table of contents
- Two Pointers
- Fast and Slow Pointers
- Sliding Window
- In - Place reversal of Linked List
- Modified Binary Search
- Islands (Matrix Traversal)
- Merge Intervals
- Two Heaps
- Top 'K' Elements
- K-way Merge
- Cyclic Sort
- Breadth-First Search (BFS)
- Depth-First Search (DFS)
- Topological Sort
- Fibonacci Number
- Subsets
- 0/1 Knapsack
- Palindromic Subsequence
- Longest Common Substring
- Bitwize XOR
Two Pointers
It is used when we need to find pairs or sub-arrays in an array that satisfy a certain condition, or when we need to find a specific element in a sorted array.
Typically, the two pointers advance towards opposite ends of the data structure with a fixed increment.
Data Usages: Arrays, Linked List, Strings

Sample Problems
Two Sum ➡️ Solution
Two Sum II - Input Array is Sorted
Longest Palindromic Substring
Maximum Sum Subarray
Intersection of Two Linked Lists
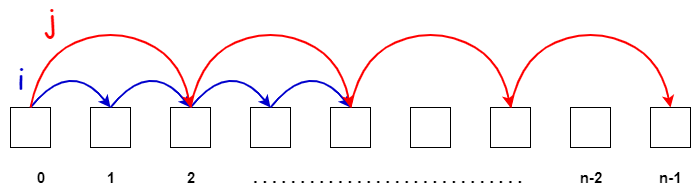
Fast and Slow Pointers
It is used in DSA to solve problems involving linked lists, arrays, or other data structures where we need to iterate the data in a specific way.
The Fast and Slow Pointer technique involves using a "slow" pointer and a "fast" pointer. The slow pointer moves one step at a time, while the fast pointer moves two steps at a time.
Data Usages: Arrays, Strings, Linked Lists
Sample Problems
Linked List Cycle
Middle of a Linked List
Intersection of Two Linked Lists
Remove Nth Node From End of List
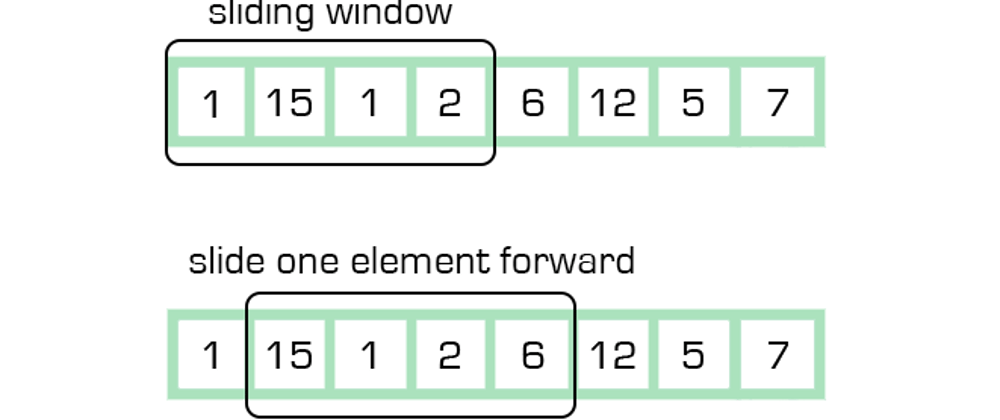
Sliding Window
It is used when we need to find a subarray or a substring that meets certain criteria, such as having a specific sum or product or containing a certain pattern or character and the input data in a specific window size.
Data Usages: Arrays, Strings, Linked Lists
Sample Problems
Maximum Sum Subarray of size k
Longest Substring without repeating characters
Find the Index of the first occurrence in a string
Minimum Window Substring
In - Place reversal of Linked List
It is used when we need to reverse the order of the elements in the linked list without using any additional data structures such as arrays or other lists.
DSA Usages: Linked List

Sample Problems
Reverse Linked List
Reverse Linked List II
Palindrome Linked List
Modified Binary Search
This method is used when the conventional binary search algorithm cannot be used to solve the problem because the search condition is more complex than simply checking if an element is greater than or less than the middle element.
Data Usages: Arrays
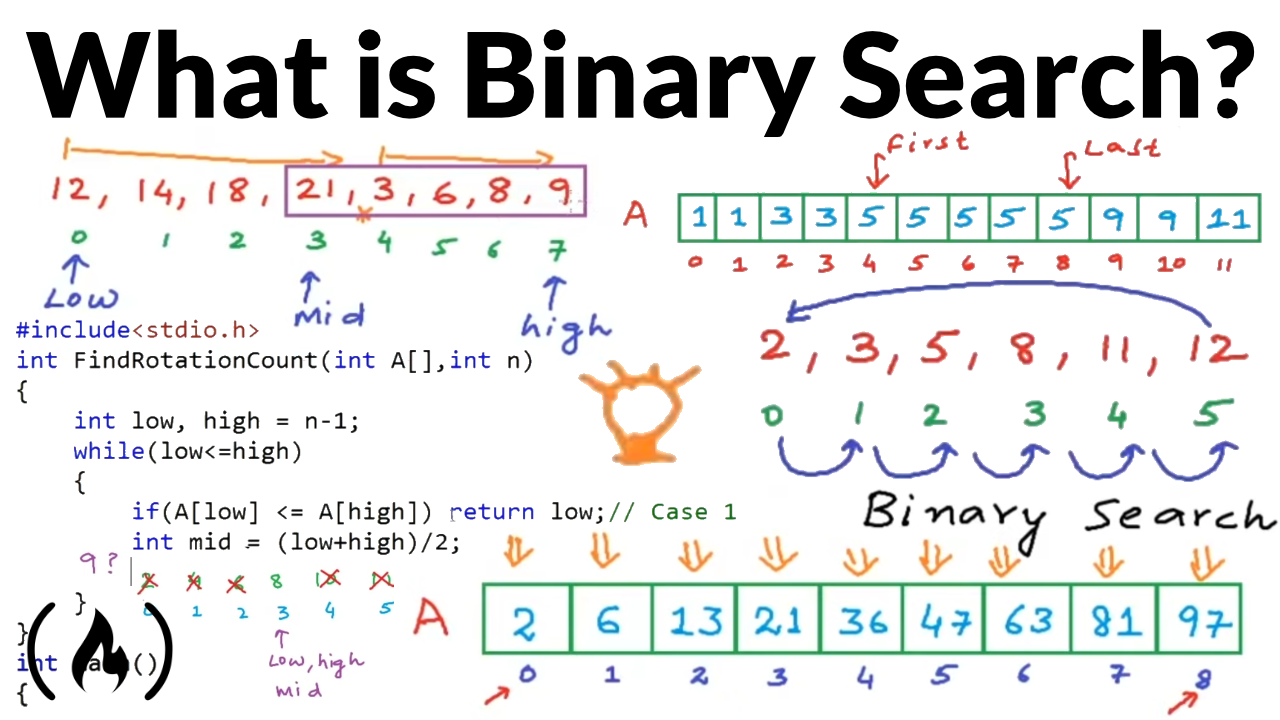
Sample Problems
Find the Minimum in a Rotated Sorted Array
Find the First and Last Position of the Element in the Sorted Array
Search a 2D Matrix
Islands (Matrix Traversal)
It is used to solve problems that involve traversing a matrix or grid to find a specific pattern or object. This method is used when the problem requires identifying clusters or groups of cells in the matrix that meet certain criteria.
Data Usages: Matrix, Queue
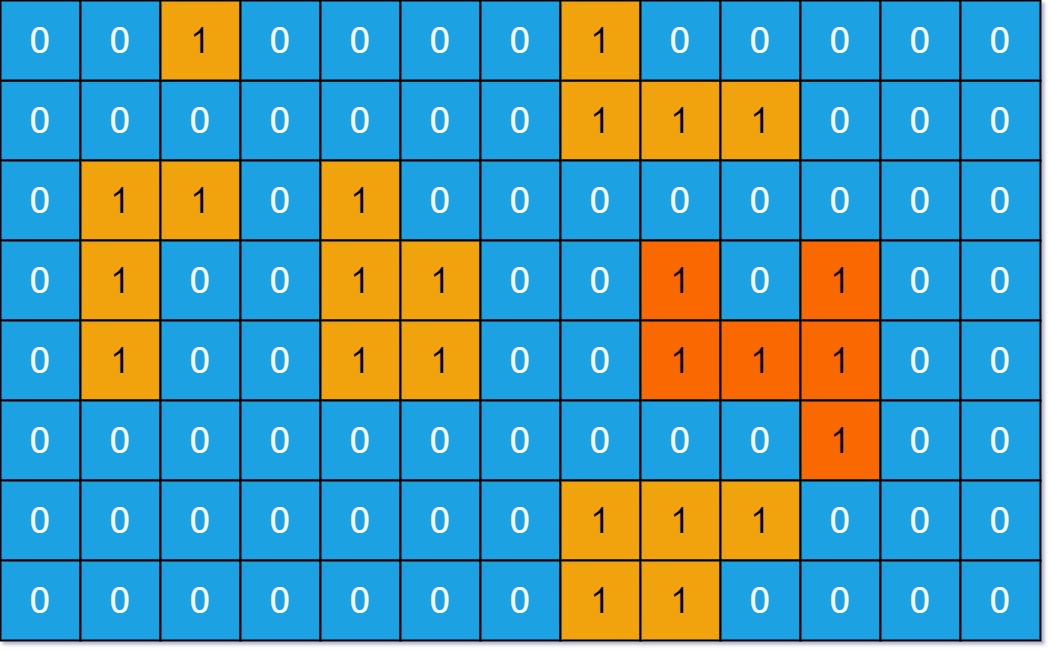
Sample Problem
Number of Islands
Longest Increasing Path in a Matrix
Count Submatrices with all ones
Merge Intervals
The Merge Interval is a popular method for solving problems that involve merging or overlapping intervals. It is used when the problem requires combining or merging intervals that share a common overlap or intersection.
Data Usages: Array, Heap

Sample Problems
Merge Intervals
Non-overlapping Intervals
Insert Intervals
Meeting Rooms
Interval List Intersection
Two Heaps
The Two Heaps is a popular method for solving problems that involve managing and processing elements in two separate heaps simultaneously. It is used when the problem requires maintaining two sets of elements with specific ordering or prioritization properties.
Data Usages: Heap, Array
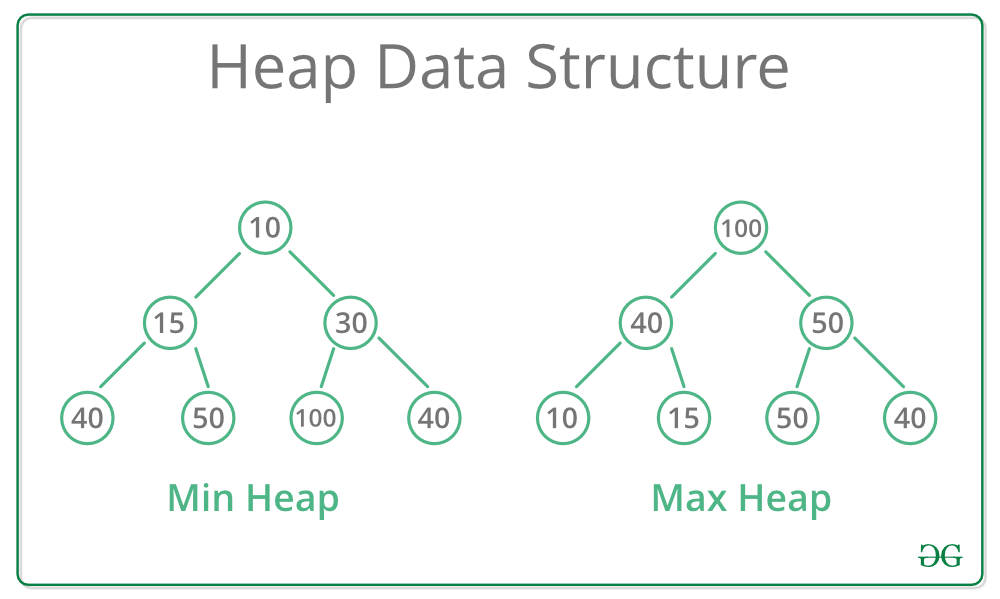
Sample Problems
Find Median from Data Stream
Kth Smallest Element
Sliding Window Median
Top 'K' Elements
The Top 'K' Elements is a popular method for solving problems that involve finding or managing the K largest or smallest elements from a collection of elements. It is used when the problem requires identifying the elements with the highest or lowest values based on a specific criterion.
Data Usages: Heap, Arrays
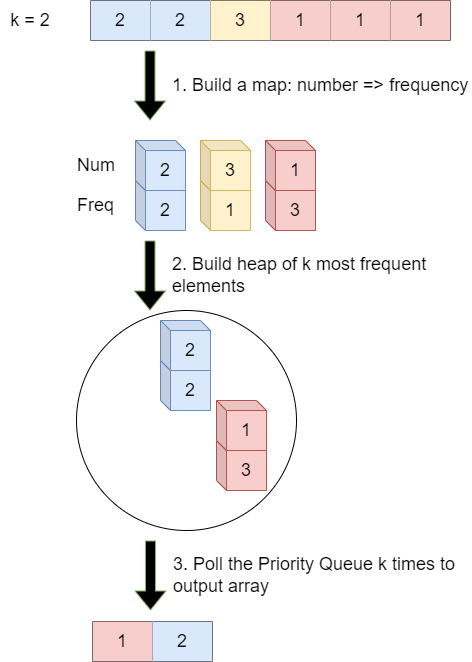
Sample Problems
The least number of Unique integers after k removal
Top K Frequent Elements
K Closest Points to Origin
K-way Merge
The K-way Merge is a popular method for solving problems that involve merging multiple sorted lists or arrays into a single sorted list or array. It is used when the problem requires combining and sorting elements from multiple sources.
Data Usages: Arrays , Queue, Heap
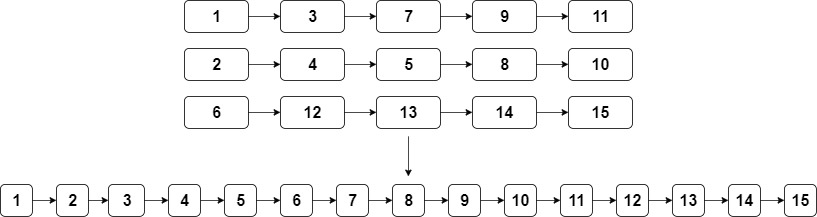
Sample Problems
Merge K-Sorted Lists
Kth Smallest value in a Sorted Matrix
Cyclic Sort
The Cyclic Sort is a popular method for solving problems that involve sorting an array of numbers in a specific range. It is used when the problem requires arranging the elements of the array cyclically to achieve the desired order.
Data Usages: Arrays

Sample Problems
Missing Number
Sort Colors
Breadth-First Search (BFS)
BFS is a popular method for solving problems related to traversing or searching in a graph or tree data structure. It is used when the problem requires exploring or visiting all the vertices or nodes of the graph in a breadth- wise manner, i.e., exploring the vertices at the same level before moving to the next level.
Data Usages: Trees, Graphs, Matrix, Queues

Sample Problems
Shortest Path Visiting All Nodes
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
Minimum Depth of a Binary Tree
Populate Next Right Pointer in Each Node
Depth-First Search (DFS)
DFS is a popular method for solving problems related to traversing or searching in a graph or tree data structure. It is used when the problem requires exploring or visiting all the vertices or nodes of the graph in a depth-wise manner, i.e., exploring as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
Data Usages: Tree Graph Matrix
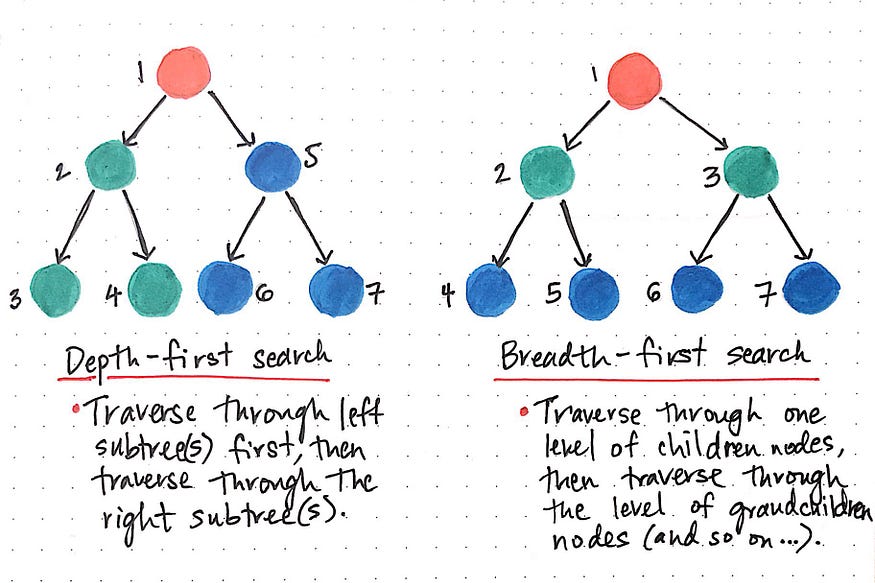
Sample Problems
Count Number of Complete Components
Find Number of Connected Components in an Undirected Graph
Topological Sort
The Topological Sort is a popular method for solving problems related to directed acyclic graphs (DAGs). It is used when the problem requires ordering the vertices of a DAG in such a way that for every directed edge (u, v), vertex u comes before vertex v in the ordering.
Data Usages: Arrays hash Table Queues Graphs
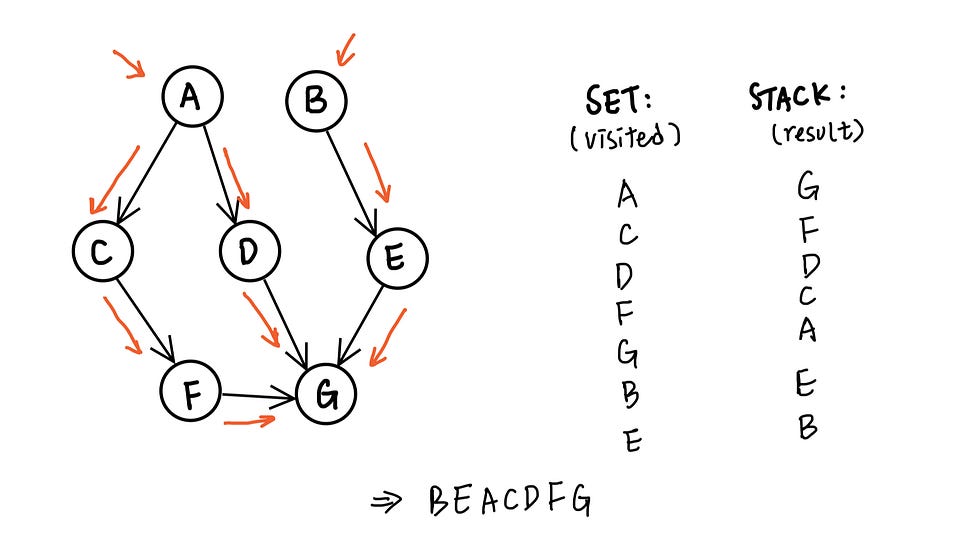
Sample Problems
Course Schedule II
Verifying an Alien Dictionary
Path Sum III
Fibonacci Number
The Fibonacci Numbers method is a mathematical sequence that is frequently used in DSA to solve various problems. It is used when the problem involves calculating or generating the Fibonacci sequence or utilizing the properties of Fibonacci numbers.
Data Usages: Arrays, Hash Table
Sample Problems
Fibonacci Number
Climbing Stairs
Subsets
The Subsets method is a common algorithmic approach used in DSA to generate or explore all possible subsets of a given set. It is used when the problem involves finding or generating all combinations or subsets of elements from a set.
Data Usages: Queues, Arrays, Strings
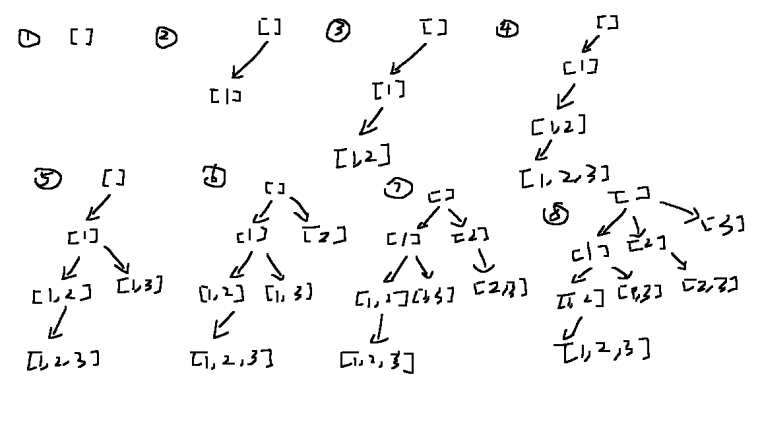
Sample Problems
Subsets
Subset Sum Problem
Permutations
0/1 Knapsack
The 0/1 Knapsack method is a well-known algorithmic approach used in DSA to solve optimization problems, particularly those involving resource allocation or selection. It is used when the problem requires maximizing or minimizing a value while considering constraints on the capacity or availability of resources.
DSA Usages: Array, HashTable
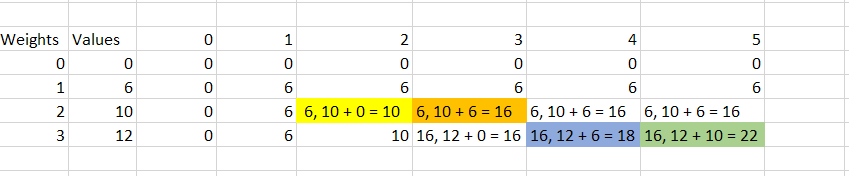
Sample Problems
Target Sum
Palindromic Subsequence
The Palindromic Subsequence method is a technique used in DSA to solve problems that involve identifying and manipulating palindromic subsequences within a given string or sequence. It is used when the problem requires finding or manipulating palindromic subsequences with specific properties or constraints.
Data Usages: Array, HashTable
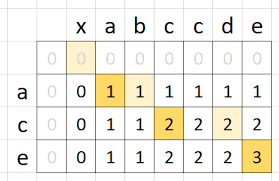
Sample Problems
Longest Palindromic Subsequence
Count Different Palindromic Subsequences
Minimum Insertion Steps to make a String Palindrome
Longest Common Substring
The Longest Common Substring method is used in DSA to solve problems that involve finding the longest common substring between two or more strings. It is used when the problem requires identifying the longest continuous sequence of characters that is common to multiple strings.
DSA Usages: Array, HashTable
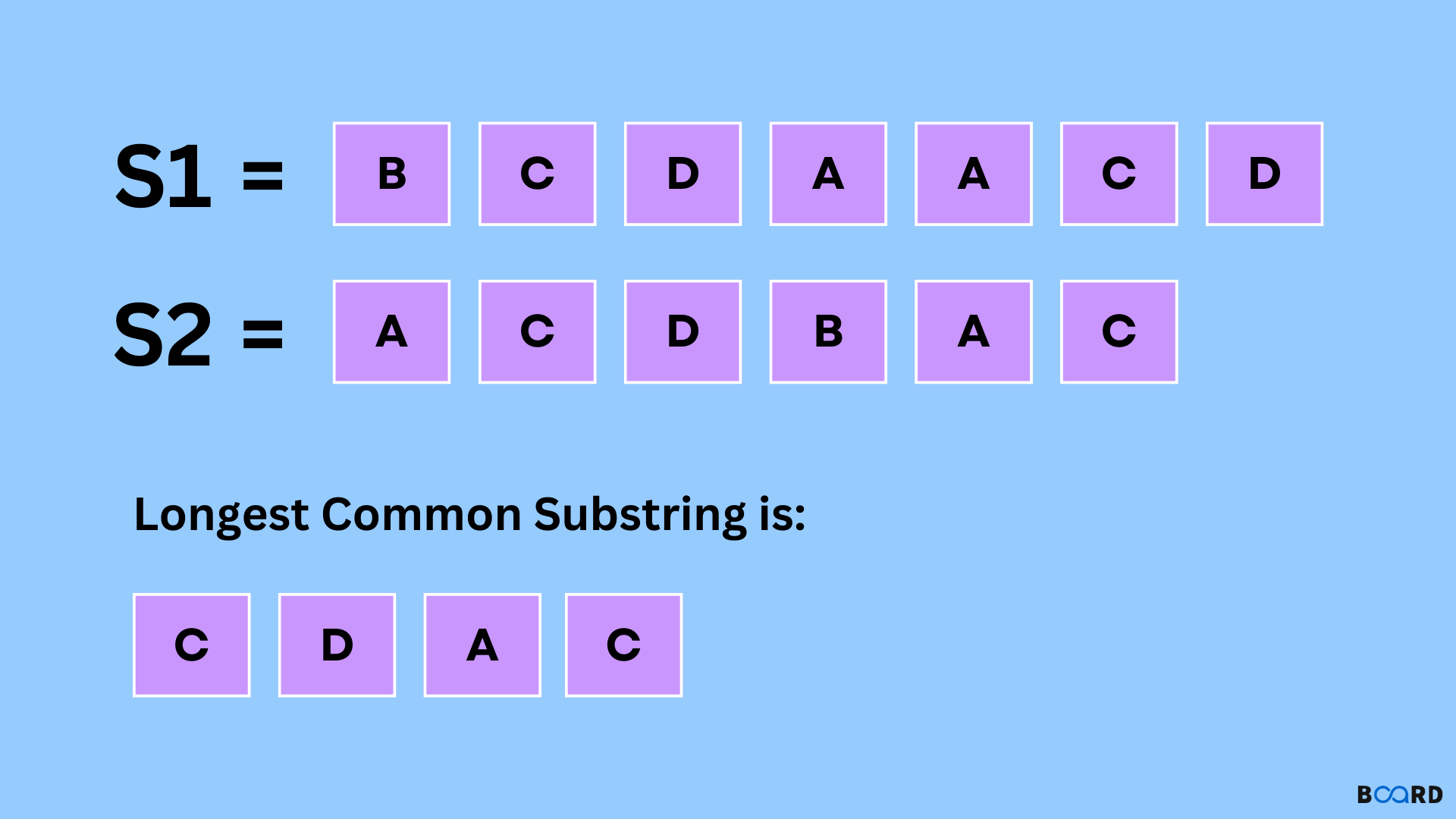
Sample Problems
Longest Common Subsequence
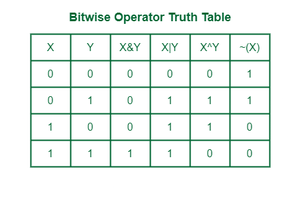
Bitwize XOR
The Bitwise XOR (Exclusive OR) method is used in DSA to solve various problems that involve bitwise operations and manipulation of binary representations of numbers. It is used when the problem requires performing operations or extracting information by manipulating individual bits using XOR logic.
Data Usages: Arrays, Bits